Knee Osteoarthritis
What is it?
Knee osteoarthritis occurs when the cartilage in the knee wears down causing friction at the knee joint. This cartilage may wear down until the bones are rubbing together without the protection of the cartilage. Knee osteoarthritis can occur to the inside of the knee, outside, or both. To diagnose knee osteoarthritis, your doctor may send you for an x-ray. This may also determine if one side of the joint is narrower than the other, which can help with the treatments.
Causes?
Age
Because osteoarthritis occurs when the joint is worn down, this does happen over time. The more stress we put on our joints, the faster they will wear out. This stress may be exaggerated by factors such as the way you are walking, and previous injuries.
Abnormal Gait
When our feet are moving abnormally, this influences the structures up the chain. Your feet are like the foundation of your house; if the foundation is not level, the house may need fixing earlier than a house with a level foundation. Your feet are the same; if they are not “level”, your knees and hips start to wear down faster. Two of the common ways to talk about your feet are pronation and supination. Pronation is when the feet roll in, whereas supination is when the feet roll out. Both of these are detrimental to the knee joint, as they contribute to excessive motion and compression to the knee joint.
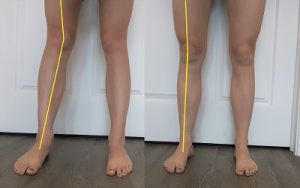 Pronation is detrimental because when the feet roll in, so does the lower (tibia) and upper (femur) leg. This puts strain on the knee joint by excessive motion or pressure to one side of the knee. Pronation also leads to knocked knees (valgus alignment). This is when the knees are pointing towards each other, which causes the outside of the knee joint to narrow compared to the inside.
Pronation is detrimental because when the feet roll in, so does the lower (tibia) and upper (femur) leg. This puts strain on the knee joint by excessive motion or pressure to one side of the knee. Pronation also leads to knocked knees (valgus alignment). This is when the knees are pointing towards each other, which causes the outside of the knee joint to narrow compared to the inside.
Supination is detrimental in the opposite way as pronation. When the feet roll out, this causes strain and pressure to the opposite side of the knee. It leads to bowed legs (varus alignment), where the knees are pointing away from each other. This narrows the joint space on the inside of the knee. Supination may also lead to limited shock absorption. The shock needs to go somewhere, and the knee joint may take some or most of this.
When your joints have this increased motion or pressure, they may wear down faster and cause pain.
Previous injury
Injuries from the past may not be affecting your day to day life, but may become relevant later in life. If the joint becomes injured and does not heal properly, there is less in the joint to wear out. Even with injured structures around the joint, this may increase movement or pressure to the joint, which increases wear and tear.
Rheumatoid vs Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic disease, where the body attacks multiple joints in the body. These joints become red, swollen, painful, and stiff. The damage occurs from inside the body.
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease, where the joints wear down due to mechanical factors.
What Will I Feel?
Knee osteoarthritis creates pain in the knee joint. Depending on the severity, this pain can be during certain activities or throughout the entire day. The knee joint may also be tender to the touch, swollen, and have less motion (stiff). There may also be crepitus in the knee joint, which is a grinding or crackling type noise while moving the joint.
How do I reduce the pain?
Orthotics
When your gait/walking is contributing to knee osteoarthritis, foot orthotics help prevent more wear and tear on the joint and reduce the pain. Orthotics prevent excessive motion at the knee by controlling the pronation or supination. Orthotics can also be used to angle the knee and release pressure to one side of the knee. To see if orthotics is right for you and your knee osteoarthritis, an assessment is recommended.
Knee Braces
Knee braces help to control the knee directly. There are different kinds of braces to help with different symptoms. Certain braces will contain compression to relieve swelling, while others will open up one side of the knee to relieve pressure.
Proper Footwear
Proper footwear can make a large difference in knee osteoarthritis. Look for a cushioned midsole for shock absorption and a good base of support for stability and to reduce excessive joint motion.
Other (Non-pedorthic related)
There are other treatment options for knee osteoarthritis that fall out of the scope of a Pedorthist.
Physiotherapists will help to rehabilitate and provide strength for the joint, among other treatments. Exercise is important because it strengthens the muscles around the joint and helps to lubricate the joint space. A physiotherapist would be able to provide more information about this.
Surgery is common once the cartilage has completely worn out. Speak to you doctor or orthopaedic surgeon if you believe this is right for you.
Another alternative therapy includes a fluid injection into the joint. This provides relief from the joint rubbing together. Talk to your doctor for more information.
If you have additional questions, feel free to contact us!

You must be logged in to post a comment.