Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS)
What is Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome?
Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS) is pain at the patellofemoral joint. This joint is the contact point between the knee cap (patella) and the upper leg bone (femur). The knee cap (patella) is imbedded into the quadricep muscle, which will be important to remember when we talk about the cause of pain.
When you bend and straighten your knee, the patellofemoral joint is in motion. If there is damage to this joint, or the patella is not tracking properly against the femur, pain may develop.
Causes of Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
Because structures in the body are connected to each other, what happens at the feet do affect structures up the chain, such as the knee. This is also the case from the top down. What happens at the hips can affect the knees. Both the feet and the hips can be contributing to the knee pain. One may have caused the other, but sometimes it can be hard to determine which one came first.

Mechanics
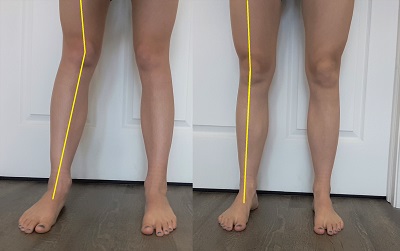
Looking at the feet, pronation and/or flat feet rotate the lower (tibia/fibula) and upper (femur) leg inwards. When they rotate in, the knee cap (patella) also rotates in, causing the joint to be in the improper position. Contributing to the misalignment are the quadricep muscles (on the front of the thigh). The quadriceps contain a group of four muscles. Three of these muscles are pulling the knee cap (patella) slightly outside, where only one is opposing these muscles and pulling in. When the foot rolls in (pronation/flat feet), rotating the lower and upper legs in, the three muscles on the outside are at an advantage and pulling even harder on the knee cap.
Muscle Imbalances
Muscle imbalances can originate from foot pronation/flat feet, or can be from other causes. If the inner quadricep muscle is too weak, the outer quadricep muscles will pull at the knee cap (patella) causing improper tracking at the joint.
This can be caused and/or exaggerated from bad form. Squatting with the knees pointing inwards will strengthen the outside muscles and almost ignore the inside muscle. This improper squatting can begin from foot pronation, or from another cause.
A physiotherapist would have more information and treatment for muscle imbalances.
What will I feel and see?
Pain from patellofemoral pain syndrome can be felt at the front of the knee cap. This can also be felt almost “inside” the knee, or pain around the knee cap.
An indication of improper tracking at the patellofemoral joint is squatting with the knees pointing inwards. This can indicate pronation/flat feet or imbalanced quadricep muscles.
As there are other conditions leading to knee pain, speak to your doctor to confirm a diagnosis.
Pedorthic Treatments
Because there may be multiple issues leading to pain, a multidisciplinary approach may be necessary. The treatments described here are focused on pedorthic treatments, but do not include all treatments available.

Orthotics
Orthotics help to deal with any pronation and/or flat feet leading to pain from patellofemoral pain syndrome. By providing support and/or correction, the lower and upper legs rotate outwards, providing a better angle for the patellofemoral joint. To determine if custom or over the counter inserts are more appropriate, an assessment is recommended.
With the support, the muscles are able to work more efficiently, but may need additional rehabilitation to treat any imbalances. In some cases, an orthotic may be necessary to aid with muscle rehabilitation. In this case, the orthotic works to provide a mechanical advantage and optimize healing during muscle rehabilitation.
Footwear
Although proper footwear may play a smaller role in pain management, it is still important to reduce and prevent pain in the future. A supportive shoe compliments a good orthotic by providing a good base and support for the orthotic. Find a shoe with a good heel counter (strong back) and a solid midsole. There are also different types of support in running shoes, such as neutral and stability. To determine if a neutral or stability running shoe is best, an assessment is recommended.
Knee Braces
There are knee braces available that help to pull the knee cap (patella) into the most appropriate position. In some cases, the brace may not address the cause of the pain, but act as a temporary fix as rehabilitation of the muscles occur.
Other
To treat a muscle imbalance, physiotherapy would be recommended to rehabilitate the muscles.
If it sounds like the condition you have, or you would like more information, feel free to contact us!

You must be logged in to post a comment.