Stress Fractures
Stress fractures are injuries to the bone caused by repetitive stress to the area. This stress can be from direct force, or from the pull of a muscle/tendon. When the body is not able to heal itself fast enough, a stress fracture can develop.
Common Stress Fractures
Common stress fractures that can come from the feet are at the tibia, fibula, metatarsals, calcaneus and the navicular.
Tibial stress fracture (shin bone)
A tibial stress fracture is one of the most common stress fractures. The tibia is the large lower leg bone (shin), and the pain/injury typically develops at the lower two-thirds.
It is a common injury in runners because of the high forces that the tibia bone absorbs. Those with a high arch are also more susceptible to developing this stress fracture. A high arch reduces the force absorbed by the motions of the feet, and instead, the force travels to the tibia.
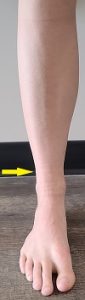 Fibular stress fracture
Fibular stress fracture
Compared to the tibia, the fibula is a smaller bone and it is located on the outside of the lower leg. The fracture/pain area is usually found at the bottom of the bone, closer to the ankle.
A very flexible and flat foot is more likely to develop this kind of stress fracture because of the force it puts onto this bone.
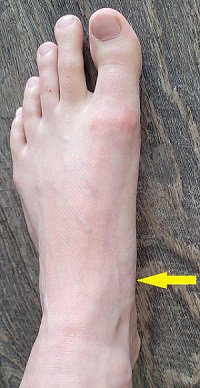
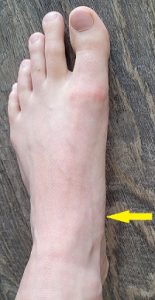
 Metatarsal stress fracture
Metatarsal stress fracture
The metatarsals are the bones through the front of the foot, behind the toes. The second and third metatarsals are the more common metatarsals to develop a stress fracture.
This kind of stress fracture is more common in walkers as well as those with a low arch, hallux valgus (big toe deviation) and a longer second toe. All of these factures place a higher stress through the metatarsal bones, especially the second and third.
Calcaneal stress fracture (heel bone)
The calcaneus is the heel bone, and is typically injured and felt at the very bottom of the heel.
This kind of stress fracture is more common in long distance runners because of the stress placed on this bone.
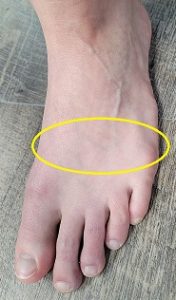
 Navicular stress fracture
Navicular stress fracture
The navicular bone is located on the inside of the middle of the foot. If you run your finger along the inside of the foot, you may feel a small bump near the arch. This is likely the navicular bone.
This kind of stress fracture is more common in those that perform explosive movements such as sprinting or jumping sports. A longer second toe can also place additional pressure on the navicular bone, making this stress fracture more likely.
Causes
Repetitive stress is the cause of a stress fracture, but what can cause that stress to occur? Stress can come from a variety of factors, such as exercise training, mechanics of the feet and poor footwear.
Exercise Training
Exercise is great for the body, but there are certain factors to be aware of to prevent injuries such as a stress fracture.
One factor to be aware of is any sudden onset or change in training. If starting a new exercise program and doing too much too soon, the body may not be able to handle the stress. Also, if there is a sudden change in the terrain, intensity or duration of the training, that can also create too much strain for the body. Gradually increasing your exercise can help to prevent stress fractures and other injuries from developing.
The training surface is another factor to consider. When possible, try to choose surfaces that have some shock absorption. Constant training on concrete or other hard surfaces can eventually take a toll on the body. At a point, the body may not be able to keep up with the healing, and lead to an injury such as a stress fracture. If you do train on harder surfaces, try to mix up the surface. Try to use grass, a track surface, or pads like a yoga mat or carpet when possible.
Mechanics of the Feet
The way your feet move can create stress related to stress fractures.
A flat foot creates excessive pull and stress to the muscles/tendons around the foot and leg. When this stress becomes too great for the body to heal, it can eventually lead to a stress fracture. A flat foot also reduces the shock it absorbs when the foot contacts the ground. Because collapse of the foot is not controlled, it may not absorb as much shock.
A high arch can also lead to a stress fracture because of the reduced shock is absorbs due to a more rigid foot structure. If this high arch is also combined with an excessive lean to the outside of the body, this can also create stress on the muscles/tendons around the foot and leg.
If your legs are two different lengths, this can also cause excessive strain to the body. In this case, it is important to determine if a lift is needed to correct the difference, or if there are other factors pulling your legs out of alignment.
Poor Footwear
Worn out or inappropriate footwear is another contributing factor for stress fractures.
Worn out footwear loses its shock absorption capabilities, as well as exaggerating the foot motions you already have. Make sure to keep an eye on your shoes and replace when necessary. For normal wear, take a look at your shoes once a year to make sure they are still in good shape.
Wearing inappropriate footwear for your feet can exaggerate the foot motions you already have or lack the support necessary for your feet. For example, if you have a high arch and you are wearing a shoe with extra support (stability), this can push your foot farther and create additional stress.
Other
Osteoporosis can also increase the likelihood of a stress fracture. Those with osteoporosis are unable to heal the body as quickly or resist as much stress put on the bones.
A stress fracture can also develop from a combination of the above factors.
What does a stress fracture feel like?
A stress fracture will typically feel like a gradual increase of pain. The pain will be felt directly in the area of the fracture. The pain will become worse as you exercise or use the area, unlike other injuries that may feel better as you warm the area up.
Pedorthic Treatments
In addition to rest and rehabilitation, there are pedorthic treatments that can help with the healing and prevention of stress fractures when the feet are involved.
Orthotics
Custom or over the counter orthotics can help with the treatment and prevention of a stress fracture. Especially when foot mechanics are involved, the support reduces the stress/strain to the area which helps with pain relief and injury healing. Even if a stress fracture has not developed yet, the proper support can help to prevent a stress fracture from developing by reducing stress to the body.
Footwear
The proper fit and shoe type are important to prevent a stress fracture, as well as helping during the healing process. Appropriate footwear will allow proper shock absorption and support to reduce stress to the body.
Shoe modifications are another option to aid with the pain and stress to the area. For example, a rocker sole is a feature that can be included in a shoe, or added on later on. It is helpful for stress fractures at the front of the foot because it reduces pressure in this area.
For more information, please contact us or book an appointment!

You must be logged in to post a comment.